What is earthing?
According to BS 7671
Connection of the exposed conductive parts of an installation to the main earthing terminal of the installation.
What is earthing system?
BS 7671 further defined
Earthing system is an electrical system consisting of a single source of electrical energy and an installation. For certain purposes, of the Regulations, types of systems are identified as follows, depending upon the relationship of the source, and of exposed conductive parts of the installation, to Earth.
The main purpose of which is to ensure safety by making the potential of all conductive parts in the system is the same with ground (zero Volts). Thus during fault there will be disconnection of supply as fast as possible.
Type of earthing system
T = Earth (from the French word Terre)
N = Neutral
S = Separate
C = Combined
I = Isolated
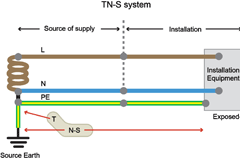
1. TN-S System
A system having separate neutral and protective conductors throughout the system.
2. TNC-S System
A system in which neutral and protective functions are combined in a single conductor in part of the system.
Both TN-S and TNC-S fall under one category which is TN and the two have common characteristics such as
Technique for the protection of persons:
- Interconnection and earthing of exposed conductive parts and the neutral are mandatory
- Interruption for the first fault using overcurrent protection (circuit-breakers or fuses)
3. TT System
A system having one point of the source of energy directly earthed, the exposed conductive parts of the installation being connected to earth electrodes electrically independent of the earth electrodes of the source.
Characteristics:
- Simplest solution to design and install. Used in installations supplied directly by the public LV distribution network.
- Does not require continuous monitoring during operation (a periodic check on the RCDs may be necessary).
- Protection is ensured by special devices, the residual current devices (RCD), which also prevent the risk of fire when they are set to ≤ 500 mA.
- Each insulation fault results in an interruption in the supply of power, however the outage is limited to the faulty circuit by installing the RCDs in series (selective RCDs) or in parallel (circuit selection).
- Loads or parts of the installation which, during normal operation, cause high leakage currents, require special measures to avoid nuisance tripping, i.e. supply the loads with a separation transformer or use specific RCDs
A system having no direct connection between live parts and Earth, the exposed conductive parts of the electrical installation are being earthed.
Characteristics:
Technique for the protection of persons:
- Interconnection and earthing of exposed conductive parts and the neutral are mandatory
- Interruption for the first fault using overcurrent protection (circuit-breakers or fuses)
Operating technique: interruption for the first insulation fault
Source:
- IET
- electrical-installation.com
- BS 7671
- City and Guilds






No comments:
Post a Comment