 MATLAB have many builtin functions to work with Excel files. In this post, we will discuss some of the common functions to work with Excel files. It is easy to interact with an excel file using xlswrite and xlsread commands. First we will make an sample excel file test.xlsx which contain grades of students in a class.
MATLAB have many builtin functions to work with Excel files. In this post, we will discuss some of the common functions to work with Excel files. It is easy to interact with an excel file using xlswrite and xlsread commands. First we will make an sample excel file test.xlsx which contain grades of students in a class.xlsread ( ) - Read Microsoft Excel spreadsheet file
The xlsread function reads data from the first worksheet of a Microsoft Excel file and save the numeric data in a array. If the file contains only numeric data the syntax is:
A = xlsread(‘filename’)
The ‘filename’ is a string with full name of the excel file (with path if the file is not in the current folder). The numeric data in the first work sheet of the file will be saved to the variable A. There are optional arguments to set the work sheet and the range to be read.
A= xlsread(‘filename’, ‘worksheet’, ‘range’)
The range is specified in the same way as represented in the excel equations (e.g. C2:F12).
If the file contains nonnumeric data, the syntax is modified as:
[NUM,TXT,RAW]=xlsread(‘filename’, ‘worksheet’, ‘range’)
The dat in the file will be saved as, numeric data in the variable NUM, text data in the variable TXT and the unprocessed data will be save as a cell array RAW. The cell array RAW will contain all the data in the worksheet.
Example:
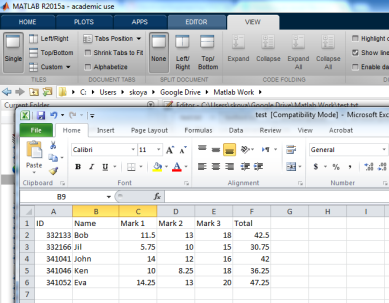
Consider the file test.xlsx, which contain the grades of students. The numeric data is stored in the range C2:F6.
>> a=xlsread('test.xlsx', 'C2:F6')
a =
11.5000 13.0000 18.0000 42.5000
5.7500 10.0000 15.0000 30.7500
14.0000 12.0000 16.0000 42.0000
10.0000 8.2500 18.0000 36.2500
14.2500 13.0000 20.0000 47.2500
To read all the data,
>> [a,b,c]=xlsread('test.xlsx')
a =
1.0e+05 *
3.3213 NaN 0.0001 0.0001 0.0002 0.0004
3.3217 NaN 0.0001 0.0001 0.0001 0.0003
3.4104 NaN 0.0001 0.0001 0.0002 0.0004
3.4105 NaN 0.0001 0.0001 0.0002 0.0004
3.4105 NaN 0.0001 0.0001 0.0002 0.0005
b =
'ID' 'Name' 'Mark 1' 'Mark 2' 'Mark 3' 'Total'
'' 'Bob' '' '' '' ''
'' 'Jil' '' '' '' ''
'' 'John' '' '' '' ''
'' 'Ken' '' '' '' ''
'' 'Eva' '' '' '' ''
c =
'ID' 'Name' 'Mark 1' 'Mark 2' 'Mark 3' 'Total'
[332133] 'Bob' [11.5000] [ 13] [ 18] [42.5000]
[332166] 'Jil' [ 5.7500] [ 10] [ 15] [30.7500]
[341041] 'John' [ 14] [ 12] [ 16] [ 42]
[341046] 'Ken' [ 10] [8.2500] [ 18] [36.2500]
[341052] 'Eva' [14.2500] [ 13] [ 20] [47.2500]
readtable( ) - Create table from file
readtable function is used to read not only excel files. \it read from different file types and sane as a MATLAB table.
T = readtable(‘filename’) is the basic syntax. There are optional arguments to set the file type and many other attributes based on the type of the file.
Example:
>> T = readtable('test.xlsx')
Warning: Variable names were modified to make them valid MATLAB identifiers.
T =
ID Name Mark1 Mark2 Mark3 Total
__________ _______ _____ _____ _____ _____
3.3213e+05 'Bob' 11.5 13 18 42.5
3.3217e+05 'Jil' 5.75 10 15 30.75
3.4104e+05 'John' 14 12 16 42
3.4105e+05 'Ken' 10 8.25 18 36.25
3.4105e+05 'Eva' 14.25 13 20 47.25
3.42e+05 'James' 12.5 13 20 45.5
3.42e+05 'Anna' 12 10.5 16 38.5
Like in the xlsread function, read table also have optional arguments to read a specific worksheet and range. For more details refer Matlab Help.




No comments:
Post a Comment